State of RNA Development: Key Considerations from Product Development to GMP
We have seen messenger RNA (mRNA)-based vaccines evolve from a potential therapeutic into a proven treatment capable of taking on a global pandemic. RNA vaccines appear to have an obvious advantage over other options because of the flexibility for tailoring RNA templates and relative development speed.
RNA drug manufacturing remains challenging at scale due to the need for consistent molecule production and efficient packaging into lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for stability and effective drug delivery. Process variables can affect the quality of the drug substance and key aspects of analytical method development must be considered to guarantee successful scale-up and initial production runs.
Critical Factors in mRNA Synthesis
One challenge in RNA process development is choosing the raw materials. Several key considerations include:
- Enzymes must be of high fidelity to minimize polymerization errors or strand breaks.
- Nucleotide Triphosphates (NTPs) must be selected carefully for drug product stability.
- DNA templates derived from a plasmid master cell bank must be pure, free from nicks and fully linearized before in vitro transcription (IVT).
Therefore, it is essential to source materials from a reputable supplier to reduce the risk of quality issues arising during RNA development or production .
A key consideration is when to add a 5’ cap, which stabilizes RNA and aids translation. Optimizing the cap sequence, reaction conditions and understanding their effects is a major challenge. Capping reactions can be performed:
- Co-transcriptionally, concurrently with IVT, which simplifies the workflow through integration.
- Post-transcriptionally, via an additional enzymatic reaction.
While producing large quantities of IVT products is not logistically challenging, 5’ IVT capping is a cost-limiting step during scale-up, even when performing co-transcriptional capping. Enzymatic capping requires efficient downstream purification to remove associated raw materials and reagents.
Downstream Processing Bottlenecks
Another major bottleneck after synthesizing the RNA is the purification steps. Unwanted contaminants from IVT must be removed, and various techniques, including precipitations, tangential flow filtration or various preparatory chromatography techniques, can be used. Developing a successful purification platform involves:
- Testing a range of methods
- Performing validations
Implementing analytical testing to verify mRNA critical quality attributes (CQAs), like identity and purity, with consistent throughput doesn’t have to be a challenge. Multi-capillary electrophoresis systems like the SCIEX BioPhase 8800 system assist in analyzing post-modification RNA lengths via parallel sample runs. The Phenomenex Biozen™ Oligo HPLC columns are perfect for high-resolution mass spectrometry for polyA tail degradation detection.
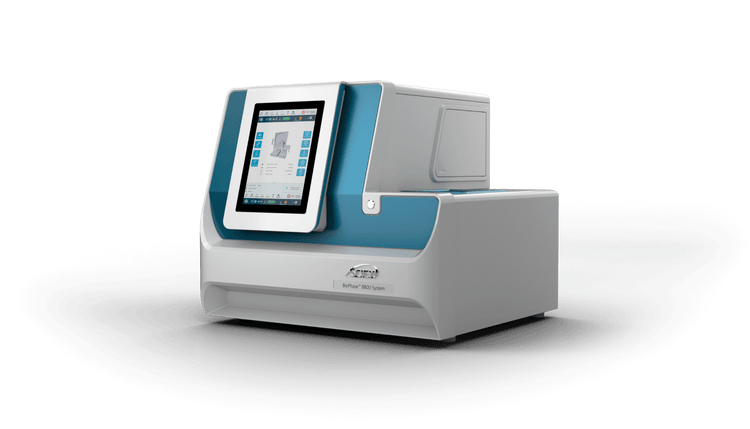

BioPhase 8800 system
New BioPhase 8800 system with Native fluorescence: Reduce the noise and up to 10x sensitivity increase without derivitization with this new multi-capillary CE system enabling high throughput protein analysis.
If you decide to outsource your GMP manufacturing to a contract manufacturing organization (CMO), Aldevron provides manufacturing capacity to address RNA scale-up and production, from obtaining linear plasmid material to full bulk drug product. They can even help with validated analytics and data management to address traceability and data sharing.

Aldevron and Integrated DNA Technologies Manufacture World’s First mRNA-based Personalized CRISPR Therapy
The Life Sciences companies of Danaher provide a wide range of personalized services and technical support to help make the transition to an integrated digital platform seamless. Contact an expert from the Life Sciences companies of Danaher today to learn more.